Positioning system has penetrated into all aspects of our life, among which satellite navigation and geographic data technology is the most mature positioning technology. However, these technologies are more suitable for use in the open outdoor environment due to the block of indoor building materials, which results in poor signal, that’s why the indoor positioning system emerged. There has been a variety of indoor positioning systems, each of which has its own suitable application industry and Bluetooth is used in a variety of industries and is considered one of the futures of IoT IPS systems. In this article, you will get to learn what IPS is, what kinds of the indoor positioning system is commonly used, why you should choose Bluetooth IPS, and how you can implement them.
What is an Indoor Positioning System?
Indoor positioning system refers to the equipment network that can locate people or objects in the indoor environment. It usually consists of two distinct elements: anchor and position tags. Anchor is a device, such as a beacon or a relay, strategically placed in a defined space. Tags are carried by people or things. Anchor either actively locates the mobile device and tag, or provides an environment location or context for the device to be aware of.
8 types of IPS ( indoor positioning system)
There are various IPS on the market. We have listed 8 commonly used indoor positioning technologies based on their signal types, among which Rf technology is the most widely used.
Radio frequency
Common RF technologies include RFID, WIFI, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and UWB. Based on RF signals, the position of a target is detected using radio signals transmitted from a transmitter to a receiver.
WIFI & Bluetooth
Wi-fi and Bluetooth can work based on existing network infrastructure. It’s easy to install and low cost. Its main working principle involves the use of received signal strength (RSS), which depends on the distance between the sender and receiver. Three measurements can be used to calculate the location of mobile devices by simply measuring the RSS of a tag to multiple Bluetooth beacons or Wi-Fi access points.
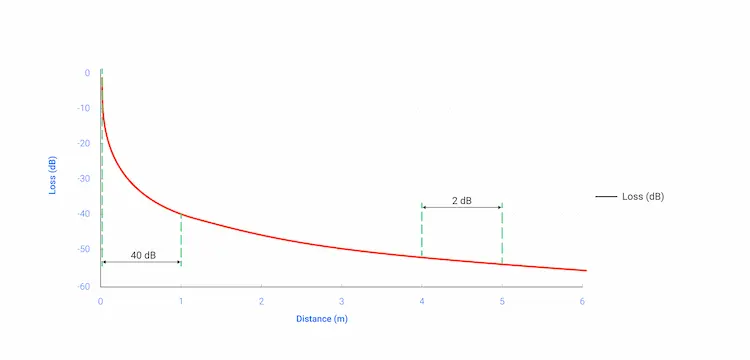
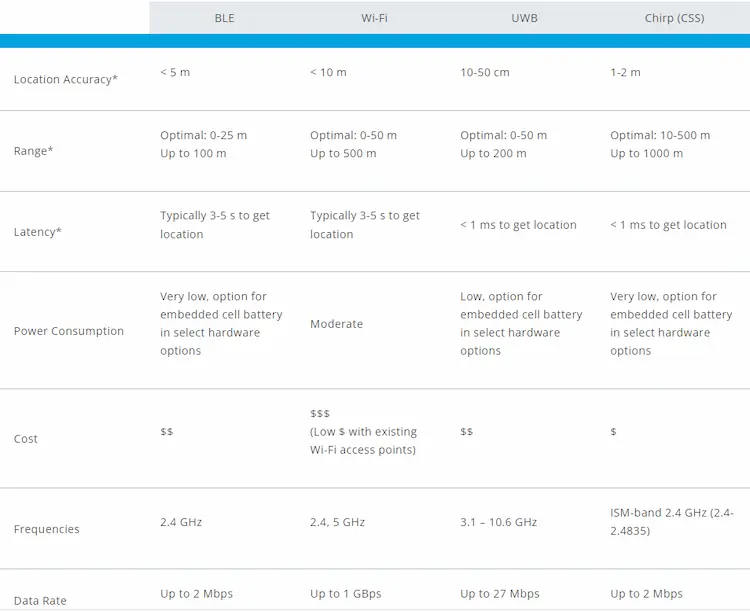
Different materials have different effects on wifi and Bluetooth signals, which affects the accuracy of signals. To overcome this problem, some IPS create RSS maps of specific areas based on specific calibrations. Their IPS accuracy can be 1-2m.
While their basic principles are the same, they are different in some points. On one hand, WIFI offers a lot of coverage while consuming a lot of power. On the other hand, Bluetooth IPS consumes less power but coverage is relatively small. Bluetooth 4.0 has an ideal maximum range of 100 m high data rates (up to 2.1 Mbps), while BLE has only around 60 m LOS and a substantially reduced data rate (125kbps).
RFID
Electromagnetic fields are used to identify and track tags attached to objects and human beings. RFID is a non-contact identification technology, it sends and receives radio frequency signals ranging from 125KHz to 5.8ghz. Readers and RFID tags formed the system. RFID is divided into three kinds, which are passive RFID, semi-passive RFID, and active RFID.
The reader sends pulses to the passive tag, which response to the reader’s request by returning ID information.
- Passive tags are cheap but can store only a few kilobytes of memory, and the reader can’t get more than a meter of information.
- The antenna and overall function of semi-passive RFID are similar to passive RFID, with battery-powering tags and other simple functions.
- Active RFID can provide a range of about 100 meters and can store more information, but it also costs more.
RFID does not need infrared systems, nor does it provide tracking information, and they may be disturbed in environments where there are liquid, metal, or other sources of radio interference.
Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-power and low-cost wireless mesh network standard for battery-powered devices used in wireless control and monitoring applications. It consists of four additional components: application layer, ZDOs, network layer, and application objects that are specified by manufacturers. The Zigbee Smart Energy 2.0 specification defines an Internet protocol-based communication protocol for monitoring, controlling, notifying, and automating the delivery and use of energy and water, of which indoor positioning is just one feature.
UWB
UWB radio frequency technology is a positioning system based on UWB. It is a radio technology for close-range, high-bandwidth communications with strong multi-path resistance properties and a degree of permeability of building materials that makes it suitable for typical indoor environments where the line of sight is normally out of sight. In addition, larger bandwidth means higher temporal resolution. This allows the time of flight between sender and receiver to be measured, resulting in better distance estimates than RSS. Therefore, the UWB system utilizes three-layer measurements to evaluate the distance of a set of at least three anchors deployed from the environment to estimate the position of tags. The UWB accuracy is currently the best among IPS, with an error of about 30-50 centimeters.
The disadvantage of UBW IPS is that it consumes a large amount of frequency bandwidth and requires special deployment. To prevent interference between other RF signals, there are legal restrictions that allow bands between 3.1GHz and 10.6GHz. The signal power is limited. If the system needs data load transmission, the working range must be limited to 100m.
Ultrasonic system
These systems rely on echolocation and measure the time period during which the emitted ultrasonic signal returns to the receiver. For example, acoustic navigation and ranging (sonar) is used to locate underwater objects. It uses the Time of Flight to calculate the distance between them. Once there are three available distances at least, you can calculate locations with Trilateration.
Ultrasound systems are not pretty commonly used in applications. The placement of multiple anchors and Bluetooth beacons are required. The accuracy can achieve sub-meter. However, ultrasonic signals tend to be affected by interference from solid materials such as buildings.
Infrared light
This IPS requires an unhindered line of sight (LOS) between the tag and anchor. It’s regarded as a very accountable room detector. Many anchors should be installed for precise positioning and may encounter difficulties because of the low quality of the signal strength measurements needed to estimate location from multiple anchors. VR headsets currently take a similar approach, using multiple light sources and reflective objects to accurately locate people in a room.
IMU
The IMU indoor positioning system includes an inertial measurement unit (IMU), which uses sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers to track the movement of objects in three-dimensional space.
Determining the direction of motion depend on the sensors, which can provide an evaluation of the relative motion of the previous position. Combining all signals with algorithms like dead reckoning can gain information.
The use of anchors in the environment is not required by IMU. However, IMU accuracy is not high as the previously introduced systems, its errors accumulate over time and reach the order of meters after a few seconds. For this reason, IMU often uses it in combination with other technologies. In addition, the ability to detect movement can be used to detect whether the participant who is wearing the tag has stopped.
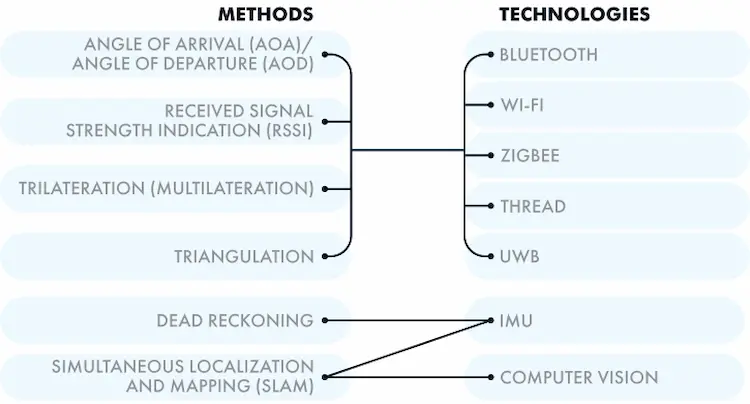
Different indoor positioning methods
To implement indoor location technology, you may need different location methods with different hardware and software solutions. Therefore, you can use labels to track moving objects, or beacons if the object is stationary. Tags are usually smaller and lighter than beacons; However, they all have a variety of configurations that vary in price and complexity. You can program the device as needed.
According to the IPS type and technology, the locating methods can be classified as follows:
AoA/AoD
AoA and AoD calculate the angle at which the signal delivered by the transmitter reaches the receiving device. They require multiple sensors and therefore require additional hardware costs, but the good point is that they provide better accuracy. AoA and AoD are usually implemented in positioning systems that use Bluetooth.
RSSI
RSSI allows the location of an object to be estimated by the strength of the signal it emits. This method is less effective due to the negative impact of stationary and moving objects around the transmitter on the signal. It is popular in wireless networks, for example, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Thread, and ZigBee.
Multilateration
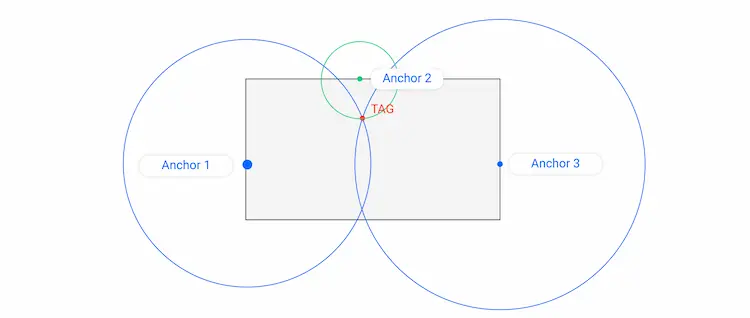
This method is applicable when the network contains three or more transport devices. You can measure the distance to the target object once the distance between some reference objects is obtained. The three-layer method involves mathematical modeling and is commonly used to improve the positioning accuracy of Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ultrasound, and UWB.
Triangulation
This is another method based on mathematical calculation. Triangulation measures the distance to an object by building triangles between reference points around it. Triangulation is an additional location method of Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and UWB systems.
Dead reckoning
This is a common indoor location tracking method used by IMU to detect the location of the target by combining the known position and speed with the track calculation. As the position error accumulates with time, the accuracy of this method is not high.
SLAM
SLAM algorithms use data from sensors or cameras to build a map of the target’s location. IMU and computer vision systems use this method to monitor the movement and location of objects.
Considerations that influence your choice of indoor positioning System technology
To determine which technology is suitable for building your own IPS, you need to consider a variety of factors and balance them according to the specifications required for the project.
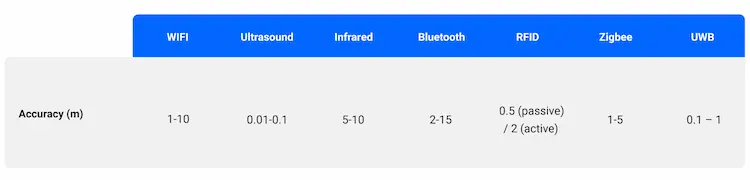
Accuracy:
Accuracy is the main feature of most indoor mapping systems. A good solution often requires flexible deployment, which adds cost and complexity. So when precise positioning isn’t a key consideration, you can opt for cheaper, simpler techniques. The table below provides the best accuracy typically obtained by several indoor positioning systems.
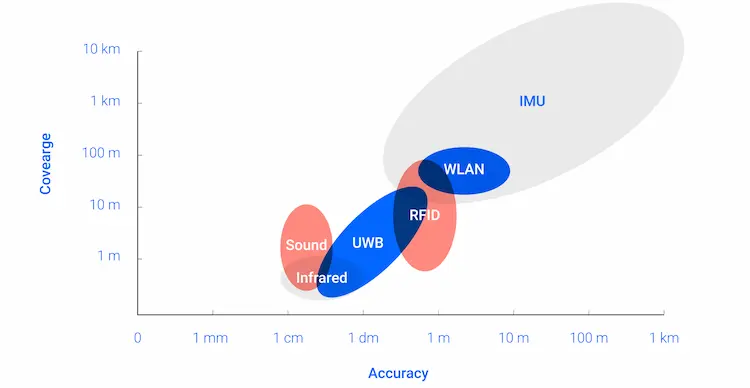
Coverage and extensibility:
Coverage is the area where location information is available. Techniques with greater coverage may mean less accuracy.
Adaptability:
Changes in the environment can have an effect on system performance. Therefore, when accuracy is required, the ability to cope with these changes is essential.
Factor sampling rate:
The number of locations obtained per second is another feature that is essential, especially for systems with complexity that need more computing power and energy.
Cost:
Deployment cost, operation cost, and maintenance cost during the system life cycle should be taken into consideration. Some technologies require a fixed installation, while others are mobile or can use existing infrastructure. Such techniques often require calibration and consume a lot of time, which results in more cost, especially when the installation is not permanent.
Why use Bluetooth IPS
Earlier versions of Bluetooth indoor location technology allowed it to be used as a proximity solution based on the RSSI approach, supported by a three-tier approach. The positioning accuracy ranges from 1 meter to several meters. The introduction of BLE technology in 2010 version 4.0 makes it a solution with low power consumption. Several of its advantages include:
- Low power consumption and low cost
This feature makes it an ideal RF standard for use in beacons, BLE sensors, and asset or personnel tags. - Easy deployment
The easy deployment and flexible hardware options can be on or independent of the network and easily integrated into the Bluetooth ecosystem. - Stretchable technology
Extend the technology to multiple location-aware use cases — from Bluetooth device detection, asset tracking, indoor location, and wayfinding to neighborhood services, etc.
Over time, the technology gained new upgrades. In 2017, Bluetooth 5 created highly scalable mesh networks that provide non-hierarchical many-to-many communication. Mesh networks can be integrated into indoor positioning systems to extend their functions and improve positioning accuracy. The release of version 5.1 in 2019 opens up more opportunities for Bluetooth location services. In addition to RSSI, the new direction-finding capability enables the system to use AoD and AoA triangulation support and detect target positions with greater accuracy. Therefore, Bluetooth 5.1 opens the door for a wide range of applications of the technology in IPS and RTLS solutions in addition to adjacent solutions.
Bluetooth IPS has some obvious strengths over other radio-based solutions. First, Bluetooth indoor positioning system is very energy efficient, which ensures the long life of wireless systems. Secondly, its new version provides advanced positioning technology and improves accuracy up to the centimeter level.
Bluetooth is everywhere. According to the Bluetooth Market Update 2020, annual shipments of Bluetooth location-based service devices grew from 4 million units in 2015 to 186 million units in 2020. That number is anticipated to reach 538 million by 2024.BLE is found in most chips and comes pre-installed in most modern mobile devices such as smartphones. This greatly simplifies technology deployment and implementation.
Below is a list of the differences between Bluetooth and other RF technology parameters so you can determine which one is right for you based on your needs.
How does Bluetooth Indoor Positioning System work?
BLE IPS solution utilizes beacons or sensors to locate and detect transmitting Bluetooth devices such as track labels, and smartphones throughout an indoor space. Location data obtained from sensors or sent from beacons to mobile devices is then absorbed by various location-based applications and translated into insights that support multiple location-aware use cases.
BLE Positioning with Sensors
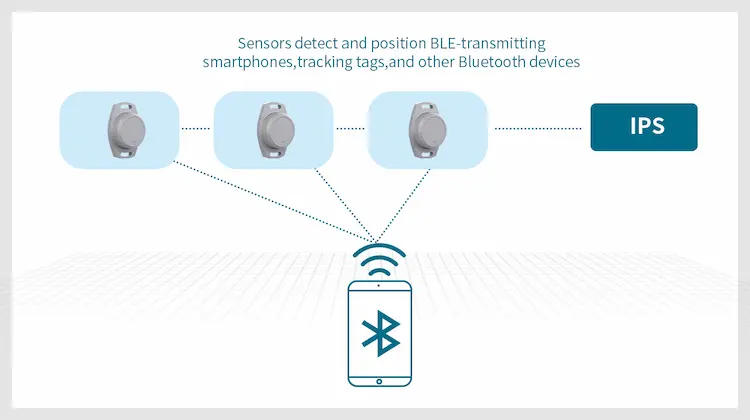
BLE sensor positioning uses BLE sensors deployed in fixed positions around the interior space. Sensors passively locate and detect transmissions of BLE smartphones, asset tracking tags, beacons, wearable, personnel location badges, and other Bluetooth devices based on the signal strength of the transmission device they receive. The location data is then delivered to a central IPS or RTLS. The positioning engine analyzes the data and uses multiple algorithms to determine the position of the transmitter. These coordinates can be utilized to visualize the position on an indoor map of your space, or for other purposes, depending on the specific location application.
BLE Positioning with Beacons
![]()
The low altitude beacon repeatedly signaled low altitude. Signals are detected by devices around, such as BLE-enabled sensors and smartphones. Deployed at fixed locations throughout the interior space, the beacon continuously broadcasts signals containing its unique identifier. This identification code is periodically sent with other data depending on the beacon communication protocol chosen. A wireless device enabled with a pre-configured service or dedicated application will receive signals from a beacon or deliver this information to a server in a server-centric manner within the beacon range. Detection between devices and beacons can enable a proximity-based location service that determines whether beacons and devices are within range of each other. Communication between wireless devices or three or more beacons can be used to pass the RSSI multinational positioning device by strategically placing multiple beacons in the interior space. The identified device location can trigger specific actions or be used for a variety of applications or services depending on the application. You can also deploy a beacon on moving objects and locate them by fixed Bluetooth sensors.
Bluetooth indoor positioning use case
There are several solutions that support Bluetooth IPS.
Asset tracking
Organizations in many industries can use Bluetooth indoor location systems to track the real-time location and status of critical assets and equipment.
- Enterprise Space: Enhance resource and productivity allocation by creating a clear picture of equipment and resources across large enterprise campuses and facilities
- Healthcare: Quickly locate and track the location of critical equipment such as wheelchairs and ventilators by adding asset-tracking capabilities
- Smart manufacturing: Creates visibility into the location and movement of devices, machines, and resources
- Warehouse management: Combines asset tracking to locate tools, inventory, and equipment throughout large facilities
Staff and personnel tracking
Organizations can utilize sensors, BLE beacons, and people tags to create visibility into employee and person locations.
- Wireless device detection: Security-conscious facilities such as corporate buildings and government can utilize sensors to detect BLE and other RF emitting devices in their interior Spaces
- Workplace Optimization: Increase productivity and operational efficiency by utilizing low-cost tags such as employee badges to give visibility into space utilization and where employees are in your space.
- Employee safety: Create safer indoor Spaces by quickly locating or notifying employees in the event of an emergency or evacuation.
- Workplace readiness: Support regulatory requirements and protocols to help prevent and mitigate the spread of disease throughout their space, use tools to allow effective hygiene guidance, contact tracing, awareness of physical distancing compliance, etc.
Location Service
By using BLE interior positioning, organizations can create smart buildings that utilize location to facilitate a variety of interactions, messaging, and other functions.
- Proximity messaging: Enhance compelling customer experiences by identifying destinations close to assets and users, and use this data to directly engage visitors with hyper-local content such as points of interest near coupon marketing campaigns
- Geo-fencing: Create virtual geographic boundaries around different areas of the interior space that trigger specific actions when the user enters, exits, or resides in a specified area
- Location sharing: Allows users to choose to share where they live, or to locate other people, including family members, friends, or colleagues, within large buildings
Indoor Navigation
The interior navigation and path-finding system via Bluetooth location makes the space instantly familiar and explorable.
- Indoor navigation: Enhance better indoor experiences for industries such as retail hotel transportation, corporate healthcare, etc.
- Blue Dot navigation: With BLE beacons and other indoor location technologies, organizations can use the blue dot experience for round-by-round navigation and pathfinding
Smart Business
Bluetooth IPS can be used to obtain location data that can be translated into amazing business insights. It locates and monitor the movement of people, asset, and equipment, and then analyze the data. Your business division can be smarter and more informed by creating visualizations of how visitors interact with interior Spaces.
How to implement Bluetooth indoor location
Implementing Bluetooth low energy indoor location projects will depend on your specifications, budget, and technical capabilities. The first thing you should decide is whether to build IPS from scratch or integrate it into an existing solution. The choice of your positioning method is depend on this.
If your Bluetooth version is lower than 5.1, then RSSI plus trioxide is your sole option. This approach applies to adjacent solutions intended for the following purposes:
- Sharing information;
- Locating points of interest and items;
- Enhancing services.
In one of our projects, one large shopping center applied our BLE indoor positioning solutions. Business owners use it for marketing, such as informing visitors of discounts and promotional offers. The client asked us to create an IPS with a BLE beacon that can communicate with mobile applications via Bluetooth 4.0. After the location of the application user is determined, the system can provide them with relevant information.
A mobile SDK that reads signals from transmitters and sends beacon data to the cloud is built and provided to you. To support RSSI measurements, trilateration is used to calculate the location of application users. Therefore, the positioning accuracy can reach 1 meter.
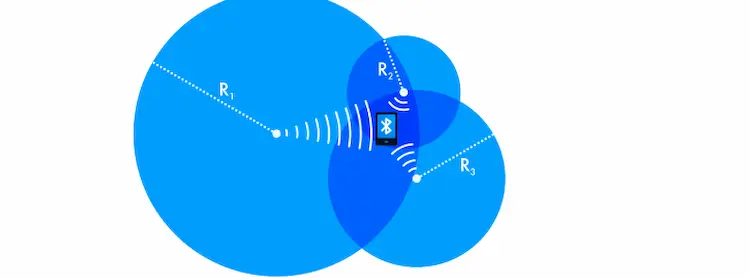
Location calculations can be done in an application or on a cloud server. Mobile devices execute this function when the network connection is unstable or unavailable. This is arduous, but there’s no need that you should always deploy the server and connect to it. If you want to build lightweight applications with low power consumption, then you can execute estimation on the server.
The number of beacons you have installed in the device is also one feature that affects positioning accuracy. Therefore, to locate the target correctly, it is necessary to ensure that the beacon density is high enough. Our Bluetooth IPS supports countless beacons at a density of at least 3-4 devices per 200m².
We used the iBeacon protocol for Bluetooth Beacon indoor location, other protocols such as AltBeacon and Google’s Eddystone can also be supported. We implemented indoor location tracking with Bluetooth proximity beacons. We added new features, extended beacon battery life, and improved the system efficiency by customizing beacons. If your system supports the latest version of the Bluetooth specification, then AoA and AoD can be your option for precise positioning in the deployment of Bluetooth location services, such as path-finding and real-time location or track.
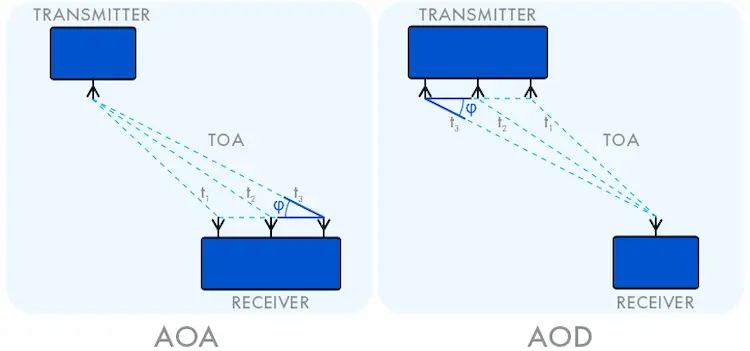
As for AoD, signals from multiple antennas at a transmitter were read by a receiver with a single antenna. Each signal reaches a certain Angle with a certain ToA. We can measure the AoD and the distance between the transmitter and receiver by knowing the distance between the transmitter antennas and the time interval between the signals.
The working principle of the AoA method is similar, but it’s in reverse: a transmitter sends signals from one antenna to multiple antennas of the receiving device.
If the network contains more than one device, triangulation can be used as an auxiliary positioning method to improve accuracy. To minimize the inaccuracy of position calculations, filtering algorithms such as Kalman filtering can be used to cross-check data.
As with any IPS, using Bluetooth for indoor locations is not a perfect solution, as it can be fraught with errors and challenges. The biggest challenge of Bluetooth IPS is detecting signals in noisy environments. Deploying a local location system in a static environment is easier. If Bluetooth IPS works in a facility or room that is full of moving objects, it is much more difficult to maintain signal integrity and locate objects correctly. This can be enhanced by increasing the number of beacons per square meter in the facility.
To ensure that your BLE-based indoor location system is working properly, you should create a detailed map of the location where you plan to deploy the system.
Conclusion
Bluetooth is a widely used IPS technology that provides connection stability with minimal power consumption. If you would like to ensure that a BLE IPS is a suitable technology for your project, don’t hesitate to contact us. We have extensive experience in building SDKS, customizing beacons, mobile applications, cloud platforms, and other solutions needed to deploy location services.



























